
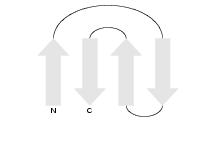
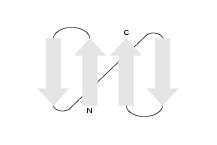
By strand orientation we mean the directions in which the strands in a
given sheet point to, following the strands along the backbone of the
protein from the N-terminus to the C-terminus. 0 is up, 1 is down. As
an example, consider the following three sheet motifs:



The first motif, the standard "up-down-up-down" motif, has the strand
orientation 0-1-0-1 (following the strand sequence 1-2-3-4). The
second motif, the "greek key", also has the strand orientation 0-1-0-1
(following the strand sequence 1-4-3-2). The third motif, for example
found in protein L, has the strand orientation 0-1-1-0 (following the
strand sequence 2-1-4-3). To take the axes of symmetry into account,
the first strand has to point up.